Attractions industry news

24 Mar 2020
Trendswatch 2020: Q&A with Elizabeth Merritt on addressing financial sustainability
In a time of financial uncertainty for the global museum community, this year's TrendsWatch report from the American Alliance of Museums (AAM) and the Center for the Future of Museums (CFM) is seeking to provoke discussion and find viable solutions to these ongoing challenges.
The report, now available, explores important cultural, technological, economic, environmental and policy events. In this year's edition, financial sustainability is addressed.
"Here at the Alliance, we know that COVID-19 is inflicting severe damage on museums," says the report's author, Elizabeth Merritt, vice president of strategic foresight and founding director for the Center of the Future of Museums.
"Our sector is just beginning to assess the impact of closures, travel bans, cancellation of major events (including fundraisers), and the implementation of social distancing. In the coming year, museums will struggle to contain the financial damage of the pandemic while supporting their staff and their communities as best they can. But even as the US makes progress towards containing the virus and rebuilding the economy, museums will find themselves in a new world when it comes to the business of running their organisations.
"Serendipitously, this year’s edition of CFM’s annual forecasting report investigates the trends destabilizing traditional income streams, documents how museums are optimising existing revenue, and highlights emerging forms of support."
With the global health crisis continuing to unfold, Attractions Management's managing editor, Tom Anstey, spoke to Merritt to learn more about this year's report and how it can help the museum sector in both the short and long term
Why did you choose to look at finance in this year's edition?
When AAM was developing its current strategic plan, we asked museums to share their biggest challenges. Financial sustainability was one of the top three issues identified by museums of all types, and that is a well-founded concern. A survey we conducted in 2017 found that 29 per cent of museums had dipped into their reserves or endowment, in the past year, to cover operating deficits. Every major museum income stream was profoundly damaged during the 2008 financial crisis, and it may be unrealistic to expect that we will ever return to 'business as usual'.
What are the key steps museums can take to try and foster financial stability?
The first step is to pay attention to information – internal and external – that can tell an organisation what is working, what is not working, and how their external business environment is changing. The second is to ensure that all staff – not just the people who work in leadership and accounting – know how to read a financial statement and understand the museum’s budget. Unless everyone – curators, educators, security staff, exhibit developers – are financially literate, how can they be expected to have ideas and make decisions that lead to financial success? The third step is to create a culture in which staff are encouraged to try experiments that may result in new ways of operating, including new income streams.
How is technology changing the way we generate funding?
Digital technologies open two massive areas of opportunity for museums – data and reach. By collecting as much information as possible on who comes to museums and how they behave, museums can tailor the experiences they create, their marketing, pricing, and their pitch for contributions in order to be as effective as possible. Social media can turn a museum’s existing fans into recruiters. Young people, in particular, are highly influenced by the recommendations of their peers when it comes to how they spend their time and money. And by providing meaningful, engaging online content, museums can win love (and support) from people who may never come through their physical doors.
What effect is unethical funding having on museums?
First and foremost, museums are having to explore what constitutes “unethical funding.” Is it funding from a source that seems to be incompatible with the museum’s own mission? Is it any wealth that results from the exploitation of people or natural resources? Is it money from people who have behaved in questionable ways in their personal lives? Since we are nowhere near having consensus on this topic as a society, whatever a museum decides, it may find itself at odds with individuals or groups who are applying a different standard. Museums will be well advised to review their policies for accepting financial support, including donations and sponsorships, and ensure they can clearly present the reasoning behind their decisions.
How does museum funding affect the workforce?
Unfortunately, the norm for nonprofits is what some have called a “poverty mindset” – spending as little as possible on “luxuries” like decent salaries and professional development. Understaffing a nonprofit, or not paying staff a fair wage just creates stressed, overworked, disaffected staff – not a more efficient and effective organisation.
Nonprofits often respond to financial stress with layoffs, salary freezes, or by letting positions go unfilled. As I point out in the report, this is counterproductive—staff are one of a museum’s most important assets, critical to its financial success. Ideally, a financially successful museum use some of those earnings to pay good wages, and provide professional development, in order to cultivate the best workforce possible.
What steps can you take if a museum isn't making enough money?
The first step is to identify who cares about what the museum is doing, and how that caring can translate into financial compensation. That might include behaving in a good capitalist manner, providing goods and services people are willing to buy at a price that supports your work. It may mean identifying the change that you can make in the world and finding a funder who shares those values. It may also require assessing how big the museum can be, and how much it can do, with the financial support it is able to muster.
What is the dominant type of philanthropy and how do you tap into that market or mindset?
Almost 70 per cent of charitable giving in the US comes from individual donors, and 20-30 per cent of that comes from people with a net worth of over $30M. The younger donors, in this pool of ultra-wealthy individuals, are less likely than their elders to fund the arts. There is an increasing tendency for funders to want to make meaningful change. Museums that can show how they contribute to progress in a cause bigger than themselves can tap into this support.
Coronavirus has had a significant effect on travel and attractions worldwide. How can a museum prepare for an event such as this in terms of finances?
A healthy operating reserve is one of the best financial preparation for business disruptions! The typical advice is to have sufficient expendable funds on hand to cover at least three months of expenses. More generally, museums can always be looking forward in time, anticipating potential disruptions—whether that is a pandemic disease, severe storms, ransomware or social unrest. Integrating a little bit of foresight into financial planning can help ensure that a museum has a business model resilient enough to weather hard times.
News powered by attractionsmanagement.com
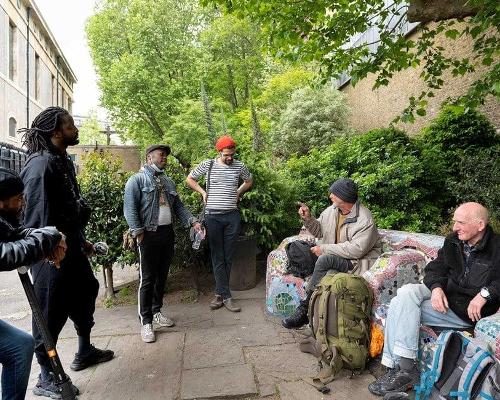

The Everyday Heritage initiative celebrates and preserves working class histories
Off the back of the success of the first round of Everyday Heritage Grants in 2022, Historic England is funding 56 creative projects that honour the heritage of working-class England. [more...]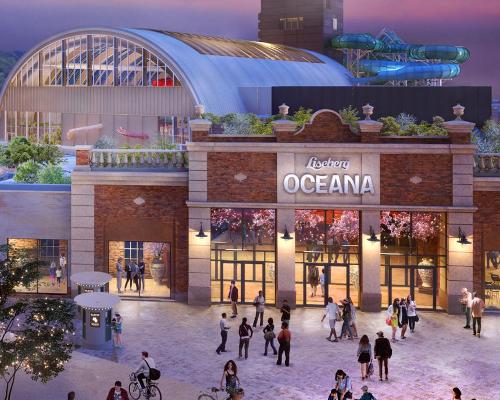
Heartbreak for Swedish theme park, Liseberg, as fire breaks out
A fire has destroyed part of the new water world, Oceana, at Liseberg in Sweden, and a construction worker has been reported missing. [more...]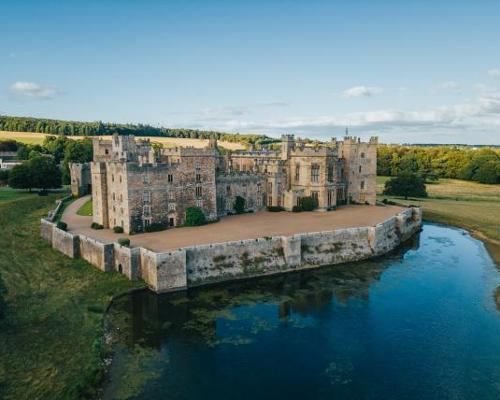
Raby Castle reveals ambitious plans to become a major visitor destination
Raby Castle, known as one of the finest medieval fortifications in England, is nearing the end of an ambitious two-year renovation project. [more...]
Wake The Tiger launches new 1,000sq m expansion
Wake the Tiger, the Bristol-based immersive art experience, is set to open its 1,000sq m expansion on Friday 2 February. [more...]
Tate Modern and Frame collaborate on a mind/body experience
London boutique operator, Frame, has teamed up with the Tate Modern to offer two yin and sound yoga classes, following by a tour of the art gallery. [more...]



















on Facebook
on Twitter